貨號
產品規格
售價
備注
BN41918R-50ul
50ul
¥1486.00
交叉反應:Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,GuineaPig) 推薦應用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41918R-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
交叉反應:Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,GuineaPig) 推薦應用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41918R-200ul
200ul
¥3490.00
交叉反應:Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,GuineaPig) 推薦應用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
產品描述
| 英文名稱 | BDNF |
| 中文名稱 | 腦源神經營養因子抗體 |
| 別 名 | Abrineurin; BDNF; BDNF; BDNF_HUMAN; Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor; Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; MGC34632; MGC34632; Neurotrophin. |
| 研究領域 | 細胞生物 神經生物學 信號轉導 生長因子和激素 轉錄調節因子 激酶和磷酸酶 細胞因子 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應 | Human, Mouse, Rat, (predicted: Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, Rabbit, Guinea Pig, ) |
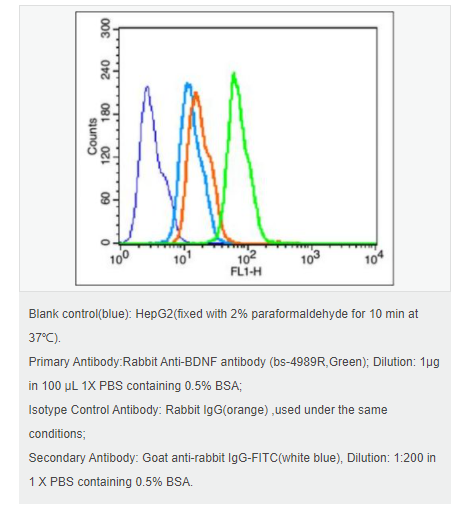
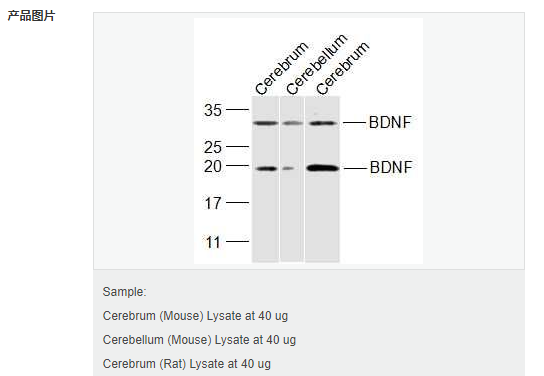
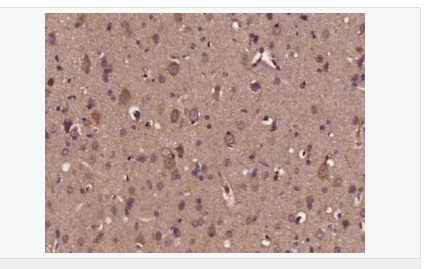
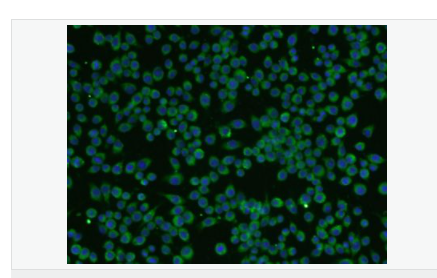
| 產品應用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 Flow-Cyt=1μg/Test ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:200-800 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 13/27kDa |
| 細胞定位 | 分泌型蛋白 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human BDNF:151-247/247 |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產品介紹 | Neurotrophins function to regulate naturally occurring cell death of neurons during development. The prototype neurotrophin is nerve growth factor (NGF), originally discovered in the 1950s as a soluble peptide promoting the survival of, and neurite outgrowth from, sympathetic ganglia. More recently, three additional structurally homologous neurotrophic factors have been identified. These include brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) and neurotrophin-4 (NT-4), also designated NT-5. These various neurotrophins stimulate the in vitro survival of distinct but partially overlapping populations of neurons. The Trk A receptor is the preferential receptor for NGF, but also binds NT-3 and NT-4. The Trk B receptor binds equally well to both BDNF and NT-4 and to a lesser extent NT-3, while the Trk C receptor only binds NT-3. BDNF promotes the survival of neuronal populations that are all located either in the central nervous system or directly connected to it. Belongs to the NGF-beta family. Function: During development, promotes the survival and differentiation of selected neuronal populations of the peripheral and central nervous systems. Participates in axonal growth, pathfinding and in the modulation of dendritic growth and morphology. Major regulator of synaptic transmission and plasticity at adult synapses in many regions of the CNS. The versatility of BDNF is emphasized by its contribution to a range of adaptive neuronal responses including long-term potentiation (LTP), long-term depression (LTD), certain forms of short-term synaptic plasticity, as well as homeostatic regulation of intrinsic neuronal excitability. Subunit: Monomers and homodimers. Binds to NTRK2/TRKB. Subcellular Location: Secreted. Tissue Specificity: Brain. Highly expressed in hippocampus, amygdala, cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Also expressed in heart, lung, skeletal muscle, testis, prostate and placenta. Post-translational modifications: The propeptide is N-glycosylated and glycosulfated. DISEASE: Defects in BDNF are a cause of congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (CCHS) [MIM:209880]; also known as congenital failure of autonomic control or Ondine curse. CCHS is a rare disorder characterized by abnormal control of respiration in the absence of neuromuscular or lung disease, or an identifiable brain stem lesion. A deficiency in autonomic control of respiration results in inadequate or negligible ventilatory and arousal responses to hypercapnia and hypoxemia. CCHS is frequently complicated with neurocristopathies such as Hirschsprung disease that occurs in about 16% of CCHS cases. Similarity: Belongs to the NGF-beta family. SWISS: P23560 Gene ID: 627 Database links: Entrez Gene: 627 Human Entrez Gene: 12064 Mouse Omim: 113505 Human SwissProt: P23560 Human SwissProt: P21237 Mouse Unigene: 502182 Human Unigene: 1442 Mouse Unigene: 11266 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications |


 、
、