貨號
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格
售價
備注
BN41071R-100ul
100ul
¥2470.00
交叉反應(yīng):Human,Rat(predicted:Mouse,Dog,Pig,Horse,Rabbit,Sheep) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,IF,ELISA
產(chǎn)品描述
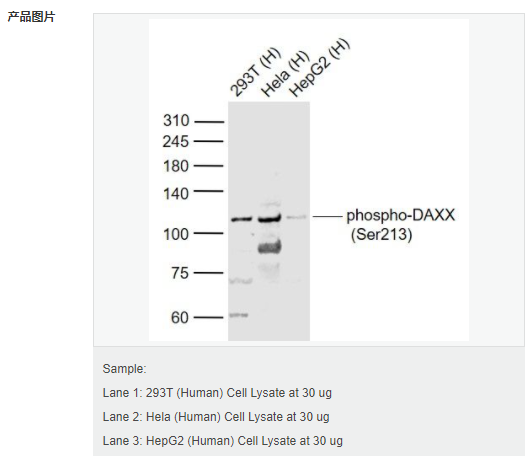
| 英文名稱 | phospho-DAXX (Ser213) |
| 中文名稱 | 磷酸化Fas相關(guān)死亡結(jié)構(gòu)域蛋白抗體 |
| 別 名 | BING 2; BING2; DAP 6; DAP6; Death associated protein 6; Death domain associated protein 6; EAP 1; EAP1; ETS1 associated protein 1; Fas death domain associated protein; hDaxx; MGC126245; MGC126246; DAXX_HUMAN. |
| 產(chǎn)品類型 | 磷酸化抗體 |
| 研究領(lǐng)域 | 腫瘤 免疫學 信號轉(zhuǎn)導(dǎo) 細胞凋亡 轉(zhuǎn)錄調(diào)節(jié)因子 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應(yīng) | Human, Rat, (predicted: Mouse, Dog, Pig, Horse, Rabbit, Sheep, ) |
| 產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復(fù)) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 81kDa |
| 細胞定位 | 細胞核 細胞漿 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated Synthesised phosphopeptide derived from human DAXX around the phosphorylation site of Ser213:DL(p-S)EL |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產(chǎn)品介紹 | Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, occurs during normal cellular differentiation and development of multicellular organisms. Apoptosis is induced by certain cytokines including TNF and Fas ligand of the TNF family through their death domain containing receptors, TNFR1 and Fas. Cell death signals are transduced by death domain (DD) containing adapter molecules and members of the ICE/CED3 protease family. A novel DD containing molecule was recently cloned from mouse, human and monkey and designated Daxx. Daxx is a death domain containing important intermediate in the Fas mediated apoptosis. Daxx binds specifically to the Fas death domain and enhances Fas induced apoptosis and activates the Jun N terminal kinase (JNK) pathway. It is widely expressed in fetal and adult human and mouse tissue, indicating its important function in Fas signaling pathways. Function: Transcription corepressor known to repress transcriptional potential of several sumoylated transcription factors. Acts as an adapter protein in a MDM2-DAXX-USP7 complex by regulating the RING-finger E3 ligase MDM2 ubiquitination activity. Under non-stress condition, in association with the deubiquitinating USP7, prevents MDM2 self-ubiquitination and enhances the intrinsic E3 ligase activity of MDM2 towards TP53, thereby promoting TP53 ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Upon DNA damage, its association with MDM2 and USP7 is disrupted, resulting in increased MDM2 autoubiquitination and consequently, MDM2 degradation, which leads to TP53 stabilization. Proposed to mediate activation of the JNK pathway and apoptosis via MAP3K5 in response to signaling from TNFRSF6 and TGFBR2. Interaction with HSPB1/HSP27 may prevent interaction with TNFRSF6 and MAP3K5 and block DAXX-mediated apoptosis. In contrast, in lymphoid cells JNC activation and TNFRSF6-mediated apoptosis may not involve DAXX. Seems to regulate transcription in PML/POD/ND10 nuclear bodies together with PML and may influence TNFRSF6-dependent apoptosis thereby. Down-regulates basal and activated transcription. Seems to act as a transcriptional corepressor and inhibits PAX3 and ETS1 through direct protein-protein interaction. Modulates PAX5 activity. Its transcription repressor activity is modulated by recruiting it to subnuclear compartments like the nucleolus or PML/POD/ND10 nuclear bodies through interactions with MCSR1 and PML, respectively. Subunit: Homomultimer. Binds to the TNFRSF6 death domain via its C-terminus and to PAX5. Binds to SLC2A4/GLUT4, MAP3K5, TGFBR2, phosphorylated dimeric HSPB1/HSP27, CENPC1, ETS1, sumoylated PML, UBE2I and MCRS1. Is part of a complex containing PAX5 and CREBBP. Interacts with HIPK2 and HIPK3 via its N-terminus. Interacts with HIPK1, which induces translocation from PML/POD/ND10 nuclear bodies to chromatin and enhances association with HDAC1 (By similarity). The non-phosphorylated form binds to PAX3, PAX7, DEK, HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, acetylated histone H4 and histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Interacts with SPOP. Part of a complex consisting of DAXX, CUL3 and SPOP. Interacts with CBP; the interaction is dependent the sumoylation of CBP and suppresses CBP transcriptional activity via recruitment of HDAC2 directly in the complex with TP53 and HIPK2. Interacts with AXIN1; the interaction stimulates the interaction of DAXX with TP53, stimulates 'Ser-46' phosphorylation of TP53 on and induces cell death on UV irradiation. Interacts with HCMV tegument phosphoprotein pp71. Part of a complex with MDM2, DAXX, RASSF1 and USP7. Part of a complex with DAXX, MDM2 and USP7. Interacts (via N-terminus) with RASSF1 (via C-terminus); the interaction is independent of MDM2 and TP53. Interacts with MDM2; the interaction is direct. Interacts with USP7; the interaction is direct and independent of MDM2 and TP53. Interacts with TP53. Interacts with human cytomegalovirus/HHV-5 protein UL123. Subcellular Location: Cytoplasm. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Nucleus, PML body. Nucleus, nucleolus. Chromosome, centromere. Note=Dispersed throughout the nucleoplasm, in PML/POD/ND10 nuclear bodies, and in nucleoli. Colocalizes with a subset of interphase centromeres, but is absent from mitotic centromeres. Detected in cytoplasmic punctate structures. Translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm upon glucose deprivation or oxidative stress. Colocalizes with RASSF1 in the nucleus. Colocalizes with USP7 in nucleoplasma with accumulation in speckled structures. Tissue Specificity: Ubiquitous. Post-translational modifications: Sumoylated with SUMO1 on multiple lysine residues. Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR. Phosphorylated by HIPK1 upon glucose deprivation. Polyubiquitinated; which is promoted by CUL3 and SPOP and results in proteasomal degradation. Ubiquitinated by MDM2; inducing its degradation. Deubiquitinated by USP7; leading to stabilize it. Similarity: Belongs to the DAXX family. SWISS: Q9UER7 Gene ID: 1616 Database links: Entrez Gene: 1616 Human Entrez Gene: 13163 Mouse Omim: 603186 Human SwissProt: Q9UER7 Human SwissProt: O35613 Mouse Unigene: 336916 Human Unigene: 271809 Mouse Unigene: 870 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |